前言
目前所有的大模型都不具备与系统交互的能力,但是我们又想要模型与系统交互,例如数据库,或者使用终端又或者写入文件等等。那应该怎么办呢?这些类似的需求促使 Tool Calling 概念出现。
文章中使用的框架版本、环境信息如下:
Lang Chain version:v0.3
Python version: v3.13
另外由于 openai , claude , grok 等这些模型对于国内并不友好。示例中我将使用 deepseek 来进行演示。
from langchain_deepseek import ChatDeepSeek
llm = ChatDeepSeek(
model="deepseek-reasoner",
temperature=0,
max_tokens=None,
timeout=None,
max_retries=2,
api_key="Your API Key",
# other params...
)
概述
其实在 tool calling 之前你会经常听到 function calling 。它们两的效果应该都是差不多的。在 langchain 中的话我们使用 tool calling 来替代它。

关键概念
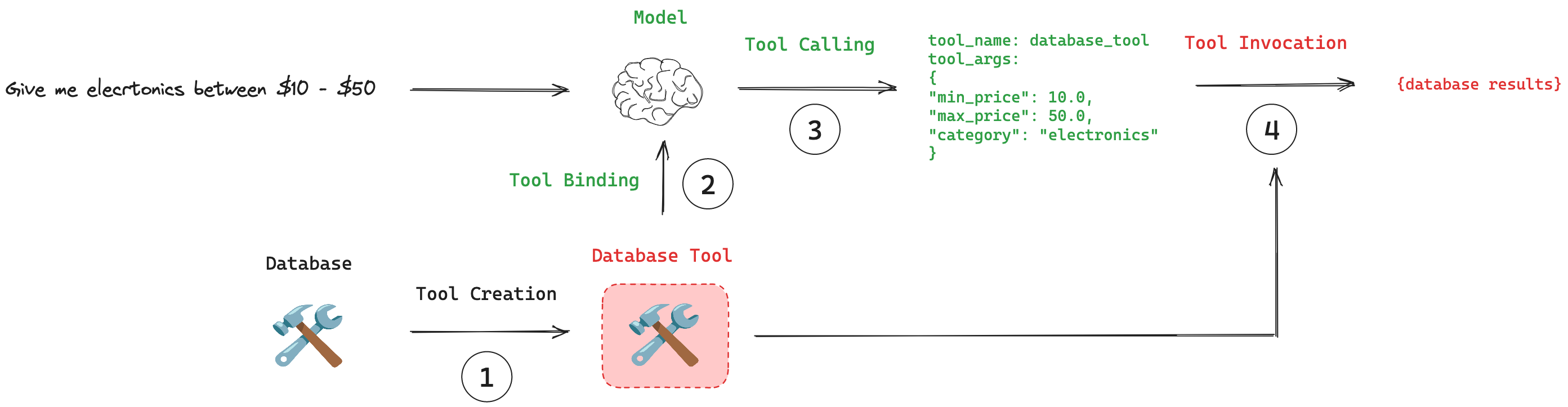
工具的使用分为以下四个步骤:
- 工具创建: 使用
@tool装饰器来创建工具。工具是一个函数。 - 工具绑定:工具需要绑定到一个支持工具调用的模型上。这使模型能够感知到工具及其所需的输入模式。
- 工具调用:当合适的时候,模型可以决定调用那一个工具。并确保其响应符合该工具的输入模式。
- 工具执行:工具可以使用模型提供的参数来执行
调用示意图如下:
推荐用法
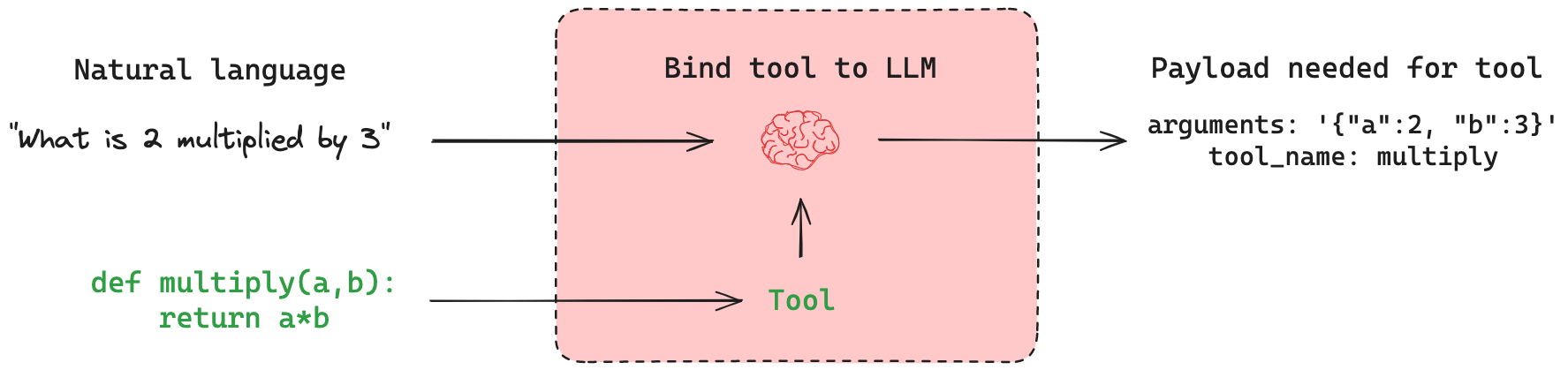
以下这段为伪代码展示了工具调用的推荐工作流程。.bind_tools()方法,表示将工具提供给模型调用。如果进行了工具调用,模型的响应将包含工具调用的参数。这些工具调用参数可以直接传递给工具。
# Tool creation
def my_tool():
pass
tools = [my_tool]
# Toool binding
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
# Tool cacalling
response = llm_with_tools.invoke(user_input)
工具创建
请注意!并非所有的大模型都支持工具调用。具体的支持列表可以查看官方文档
推荐使用 @tool 装饰器来创建工具。
from langchain_core.tools import tool
@tool
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Multiply a and b.
Args:
a: first int
b: second int
"""
return a * b
工具绑定
使用 Langchain 提供的 .bind_tools()方法将我们定义的工具提供给大模型。
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools([multiply])
工具调用
工具调用什么时候调用取决于模型根据输入的相关性决定的。模型并不是一直调用我们的工具。例如下面的示例。模型将不会调用工具。
result = llm_with_tools.invoke("Hello world!")
print(result.content)
# Output: Hello! How can I assist you today?
可以看到结果是一个APMessage,但是如果们们传递一个与工具相关的输入,模型应该会选择它调用它:
result = llm_with_tools.invoke("What is 2 multiplied by 3?")
print(result.content)
print(result.tool_calls)
# Output:
# I will calculate 2 multiplied by 3 using the `multiply` function.
# [{'name': 'multiply', 'args': {'a': 2, 'b': 3}, 'id': 'call_0_3cc82321-5246-482c-a706-5b02635cf9b8', 'type': 'tool_call'}]
因为返回的是 AIMessage 类型。如果模型调用了工具, result 将会有一个 tool_result属性,这个属性包含了执行工具所需的内容,包括工具名称和输入参数。
工具执行
工具实现了 Runnable 接口,这意味着它是可以直接被调用的。例如:
print(multiply.invoke({
'a': 2,
'b': 3
}))
# Output:
# 6
强制使用工具
有些场景你可能不希望模型自主选择工具。可以使用 tool_choice 来进行限定以达到预期的效果。例如:
from langchain_core.tools import tool
@tool
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Adds a and b."""
return a + b
@tool
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Multiplies a and b."""
return a * b
tools = [add, multiply]
llm_forced_to_multiply = llm.bind_tools(tools, tool_choice="multiply")
llm_forced_to_multiply.invoke("what is 2 + 4")
因为 deepseek-reasoner 不支持 tool_choice ,所以这里我们需要更换一下模型为 deepseek-chat .否则会有以下错误信息:
openai.BadRequestError: Error code: 400 - {'error': {'message': 'deepseek-reasoner does not support this tool_choice', 'type': 'invalid_request_error', 'param': None, 'code': 'invalid_request_error'}}
示例中即使我们告诉模型是 2加4,但是它仍然会调用 multiply 这个工具。
注意事项
在设计提供给模型的工具调用时需要注意以下几点:
- 具有明确工具调用API的模型在工具调用方面比微调的模型好。
- 工具名称和描述选择得当。表现更好。
- 简单、范围狭窄的工具比复杂工具更容易被模型使用。
- 让模型从大量工具列表中进行选择会给模型带来挑战。